Learn how to deal with datasets¶
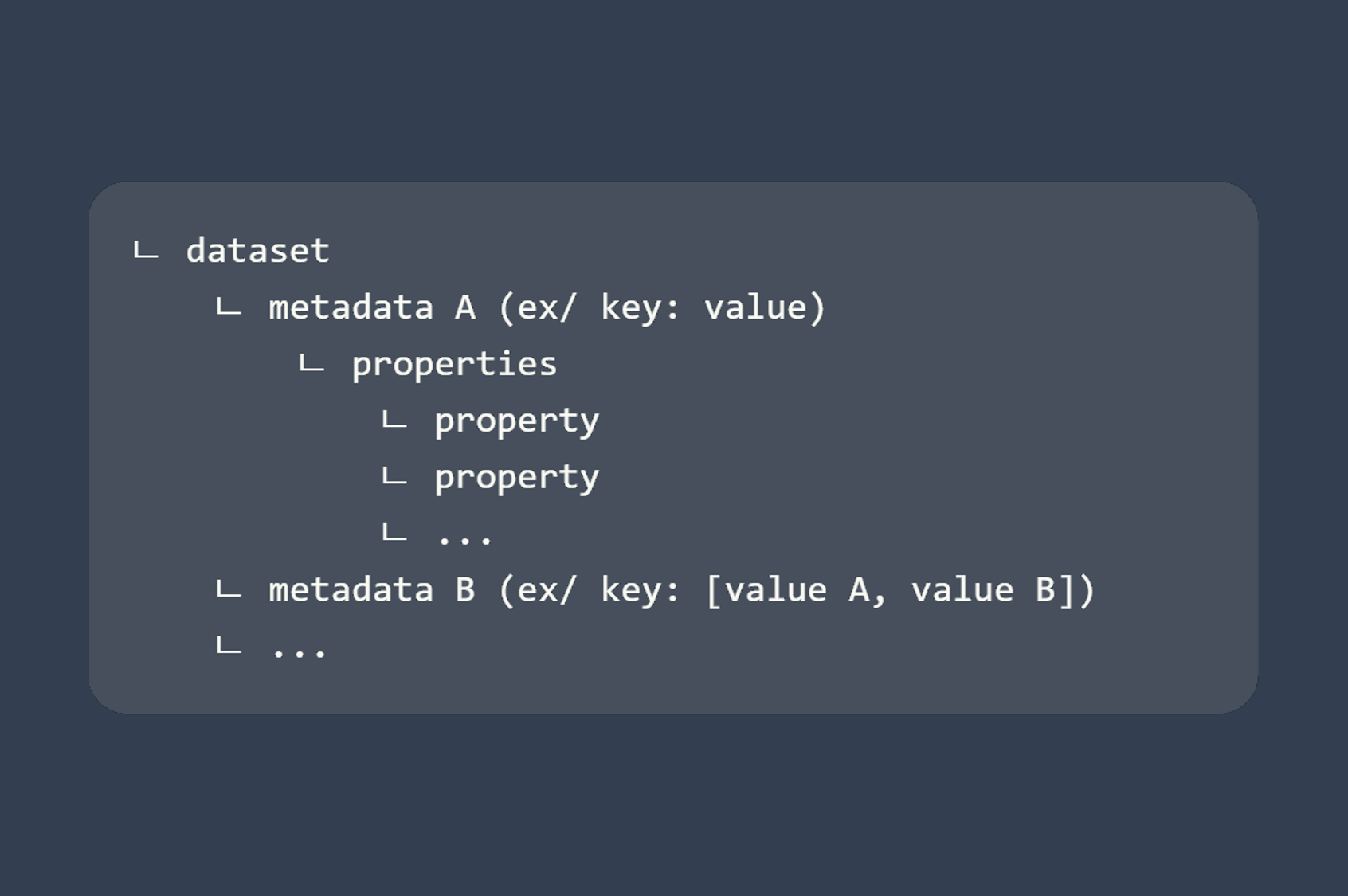
Datasets are Fast2 objects which can be involved at different levels within the punnet.
They can be found on the
- punnets
- documents
- workflows
Datasets gather data which can be manipulated to store properties, and can be accessed as follows:
DataSet dataset = punnet.getDataSet();
DataSet dataset = document.getDataSet();
DataSet dataset = workflow.getDataSet();
Since datasets are just groups of data, understanding basic operations with data is primordial.
Data object¶
In Fast2, a data has 3 different informations:
- its name,
- its type (
Stringorint) - its value(s)
The following line retrieve the data as object :
Name¶
Getting the name of a data just goes like:
Type¶
If no type has been defined when the data has been created, the data type will be null.
However Fast2 will treat the value of the data as a regular String.
Value(s)¶
When dealing with data, some can be single-valued while others can be multi-valued.
The returned object will differ accordingly.
Data values can be added along the way, even when the data has already been created with a given value to begin with:
Properties¶
A data can be dealt with just like any other object with properties.
Therefore, adding a property, removing it or getting it are just as simple as you would think:
Add data¶
Several ways of adding data to the dataset are available, depending on the type of value you are willing to store:
Data myData = myDataset.addData(name, "String", value); // String
Data myData = myDataset.addData(name, null, value);
Data myData = myDataset.addData(name, "boolean", true); // boolean
Data myData = myDataset.addData(name, type, 10); // long, int
Data myData = myDataset.addData(name, "String"); // list or arrays of String
myData.getValues().addAll(Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c"));
document.getDataSet().addData("multivalued", "String").getValues().addAll(Arrays.asList("value #1", "value #2"));
Adding a new data with the same name as an already stored one, will result in overwriting the existing value with the new one.
Iterating through all data¶
Data mapping often requires to cover all data, no matter their name. To do so, the easiest way is to get them as a list:
Retrieve data value(s)¶
The following line retrieve the data as object :
Single-valued data¶
The dataset offers a shortcut to get the value(s) of any data:
// 1st way : via data object
String value = myDataSet.getData(dataName).getValue();
// or
// 2nd way : dataset shortcut
String value = myDataSet.getDataValue(dataName);
Multi-valued data¶
// 1st way : via data object
List<String> value = myDataSet.getData(dataName).getValues();
// or
// 2nd way : dataset shortcut
List<String> value = myDataSet.getDataValues(dataName);
Remove data¶
If the data has been found and could successfully be removed, the following method will return TRUE:
Check if data exists¶
Rely on this method to make sure not to overwrite any existing data, nor having a DataNotFoundException exception.
DataNotFound exception¶
When operations are performed on non-existing data, an exception of type DataNotFoundException is thrown.